Overview
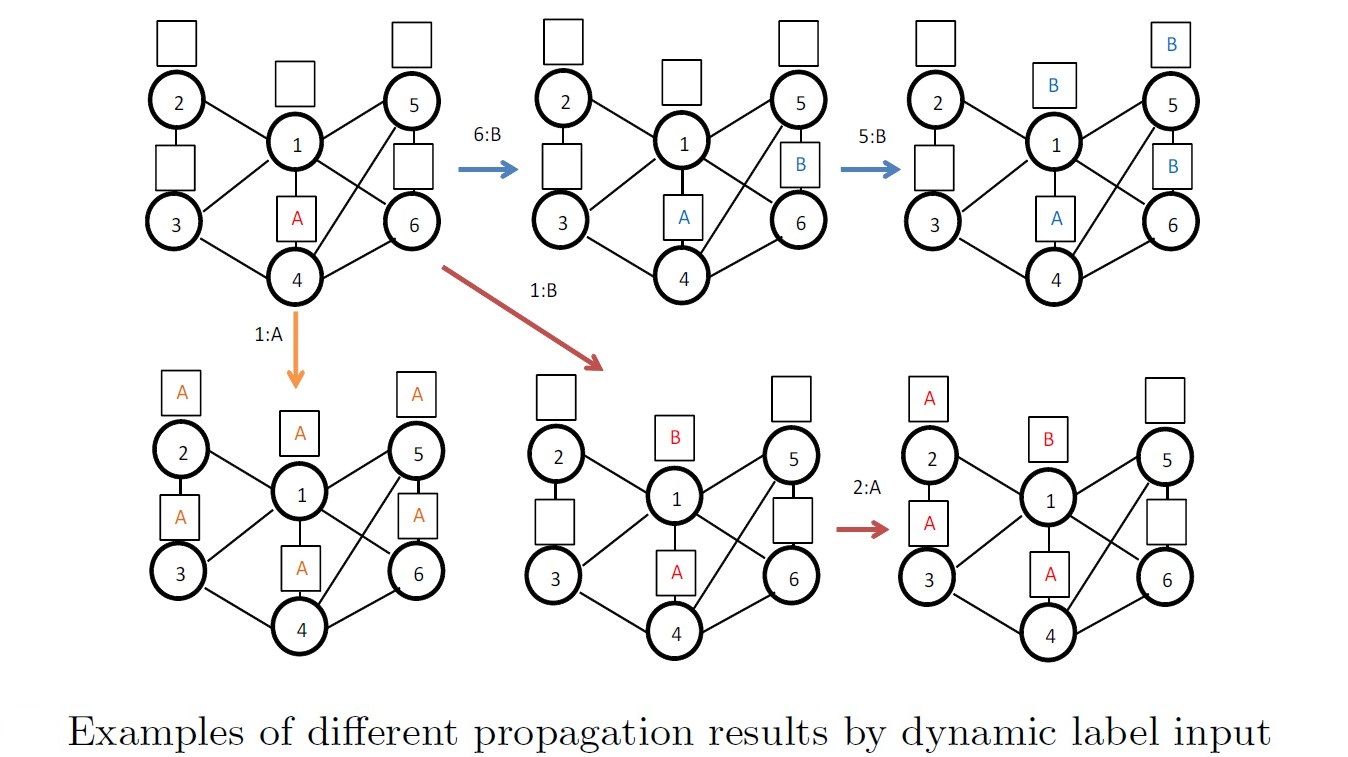
An important application of label propagation in social networks is to derive unknown node attributes from those known ones based on homophily. The often high cost of label acquisition has driven much research to find a minimal set of initial nodes to label in order to trigger the maximum propagation. A seemingly similar problem of influence maximization has been extensively studied which, however, bears critical difference from our problem. The fact that our node labels represent not just status but categorical attributes admitting all possible user assignments adds an extra dimension of problem complexity. More importantly, it calls for a new problem proposition of dynamic label propagation in which the seed set for propagation is not computed offline all at once, but, rather, incrementally with user label input at each step.
We propose the new problem definition of dynamic label propagation, present a complexity analysis of NP-hardness for problem variants and develop two greedy algorithms, G-DS and GMax-DS, based on two popular propagation models: K-nearest neighbor and linear threshold model. Furthermore, we explore the relationship between various network structure measures and the performance of our propagation results. Our empirical evaluations on real-world FreeBase data set demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our algorithm in terms of input percentage, time cost, precision and f1-score.
Members
Dataset
Publication
"Dynamic Label Propagation in Social Networks"
Juan Du, Feida Zhu and Ee-Peng Lim, The 18th International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications (DASFAA'13), Wuhan, China, April, 2013.